Somalia: A Horn of Africa Nation Navigating Instability and Resilience
Associated Articles: Somalia: A Horn of Africa Nation Navigating Instability and Resilience
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to Somalia: A Horn of Africa Nation Navigating Instability and Resilience. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Somalia: A Horn of Africa Nation Navigating Instability and Resilience
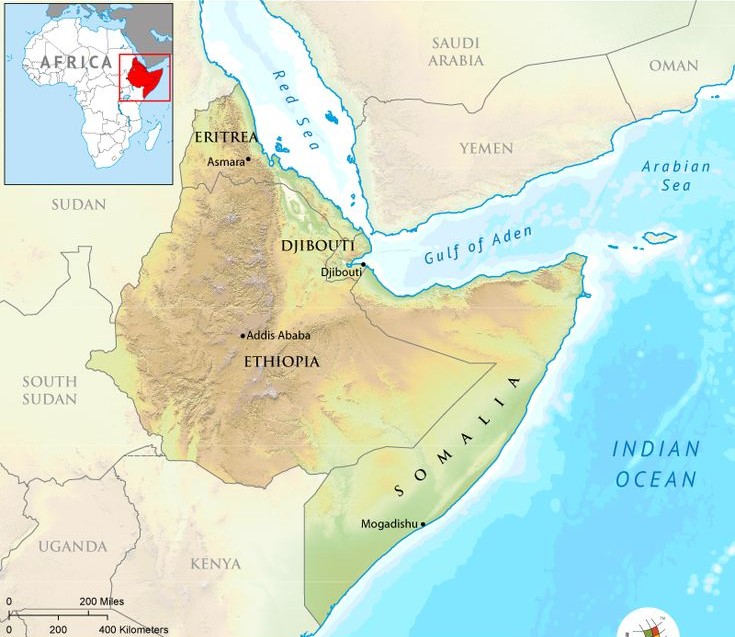
Somalia, a nation located on the Horn of Africa, occupies a strategically necessary location on the world map. Its shoreline stretches alongside the Indian Ocean, bordering Djibouti, Ethiopia, and Kenya. Nonetheless, its geographical prominence belies a posh and sometimes turbulent historical past, marked by many years of battle, political instability, and chronic challenges to its sovereignty. Understanding Somalia’s place on the world map requires extra than simply pinpointing its coordinates; it calls for an exploration of its multifaceted inner dynamics and its intricate relationships with regional and world actors.
A Geographic Overview:
Somalia’s geography considerably influences its historical past and present struggles. The nation is predominantly arid and semi-arid, with huge stretches of savanna and desert dominating the panorama. The fertile lands are concentrated alongside the rivers and coastal areas, resulting in competitors for sources and contributing to inner conflicts. The shoreline, whereas providing potential for financial improvement by way of fishing and maritime commerce, has additionally been exploited by pirates, exacerbating the nation’s safety challenges. The rugged terrain within the inside has offered refuge for varied armed teams, hindering authorities management and contributing to the persistence of inner conflicts. The nation’s various geography – from the coastal plains to the central highlands and the northern deserts – additionally displays the range of its clans and sub-clans, an important component in understanding the nation’s political panorama.
Historic Context: From Colonial Rule to Civil Conflict:
Somalia’s trendy historical past is deeply intertwined with colonialism. The nation was divided between British and Italian administrations in the course of the colonial period, a division that has left an enduring influence on its political and social buildings. Following independence in 1960, the nation initially skilled a interval of relative stability beneath a centralized authorities. Nonetheless, this stability was short-lived. The collapse of the Siad Barre regime in 1991 marked the start of a protracted civil conflict, plunging the nation right into a state of anarchy and fragmentation. The absence of a functioning central authorities led to the rise of quite a few armed teams, clan-based militias, and warlords vying for management of sources and territory. This era witnessed widespread violence, famine, and humanitarian crises, forcing tens of millions of Somalis to flee their properties, each internally and externally.
The Battle for State-Constructing and Governance:
The absence of a powerful central authorities for over 20 years has profoundly impacted Somalia’s improvement. The Transitional Federal Authorities (TFG), established in 2004, struggled to say its authority amidst the continuing battle. The formation of the Federal Authorities of Somalia (FGS) in 2012 marked a major step in the direction of establishing a extra secure political system. Nonetheless, the FGS continues to face immense challenges in extending its management all through the nation, notably in areas managed by Al-Shabaab, an Al-Qaeda-affiliated terrorist group. The continued battle has undermined state establishments, hindering the supply of important providers like training, healthcare, and safety. Corruption stays a major impediment to good governance and efficient service supply.
The Al-Shabaab Insurgency:
Al-Shabaab’s insurgency poses a significant risk to Somalia’s stability and safety. The group controls important territory in southern and central Somalia, finishing up assaults in opposition to authorities forces, civilians, and worldwide targets. Al-Shabaab’s ideology, a mix of extremist interpretations of Islam and clan-based grievances, has resonated with some segments of the inhabitants, making it a formidable opponent. The struggle in opposition to Al-Shabaab has concerned the Somali Nationwide Military (SNA), AMISOM (the African Union Mission in Somalia), and worldwide companions, however the insurgency persists. The group’s capability to adapt its ways and exploit present social and political fault traces stays a key problem for Somalia’s stability.
The Humanitarian Disaster and Growth Challenges:
Somalia has persistently confronted extreme humanitarian crises, exacerbated by recurring droughts, battle, and displacement. Tens of millions of Somalis are in want of humanitarian help, dealing with meals insecurity, lack of entry to healthcare, and displacement. The nation’s fragile financial system is closely reliant on remittances from the diaspora and restricted agricultural manufacturing. The dearth of infrastructure, together with roads, electrical energy, and communication networks, additional hinders financial improvement. The continued battle and instability have deterred international funding and hindered efforts to rebuild the nation’s infrastructure and establishments.
Worldwide Engagement and Help:
Somalia’s plight has attracted important worldwide consideration and help. The United Nations, the African Union, and quite a few bilateral companions have offered humanitarian help, safety help, and assist for state-building initiatives. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of worldwide interventions has been debated, with considerations raised about coordination, accountability, and the long-term sustainability of help efforts. The worldwide group faces the problem of balancing the necessity for safety with the promotion of human rights and good governance.
The Way forward for Somalia:
Somalia’s future stays unsure. The nation faces important challenges, together with the continuing Al-Shabaab insurgency, political instability, weak governance, and recurring humanitarian crises. Nonetheless, there are additionally indicators of progress. The FGS has made strides in establishing a extra secure political system, and the SNA has proven improved capability in combating Al-Shabaab. The Somali folks’s resilience and willpower to rebuild their nation shouldn’t be underestimated. The success of Somalia’s future will rely on a multifaceted method that addresses the basis causes of battle, promotes good governance, fosters financial improvement, and strengthens state establishments. The worldwide group’s continued engagement and assist will likely be essential in helping Somalia in its journey in the direction of peace, stability, and prosperity. Finally, Somalia’s place on the world map will likely be decided not simply by its geography, however by its capability to beat its challenges and construct a safer and affluent future for its folks. The highway forward is lengthy and arduous, however the potential for a secure and thriving Somalia stays a chance.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Somalia: A Horn of Africa Nation Navigating Instability and Resilience. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!