Map Dot Dystrophy: A Complete Overview of this Uncommon Ocular Dysfunction
Associated Articles: Map Dot Dystrophy: A Complete Overview of this Uncommon Ocular Dysfunction
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Map Dot Dystrophy: A Complete Overview of this Uncommon Ocular Dysfunction. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Map Dot Dystrophy: A Complete Overview of this Uncommon Ocular Dysfunction

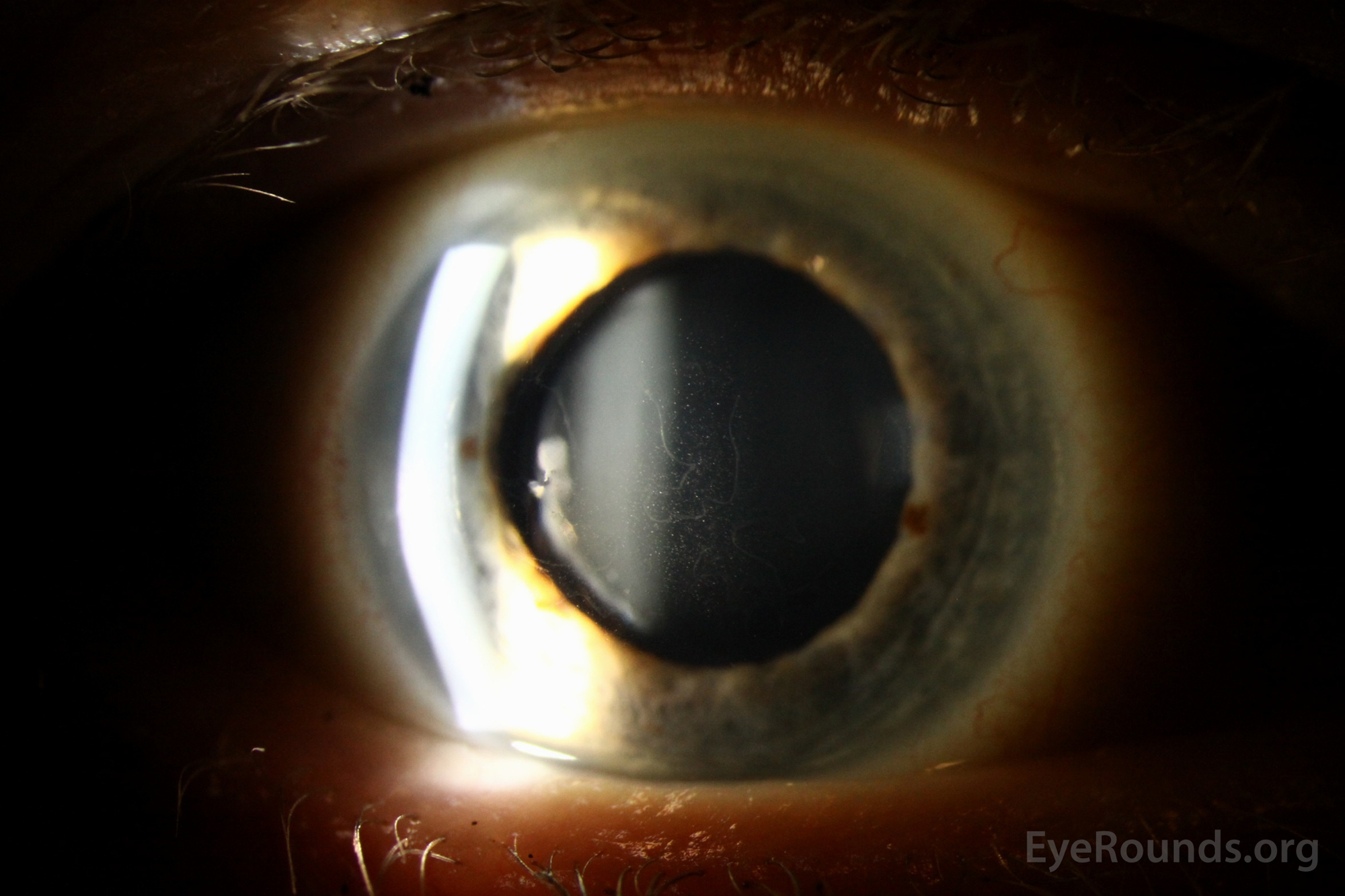
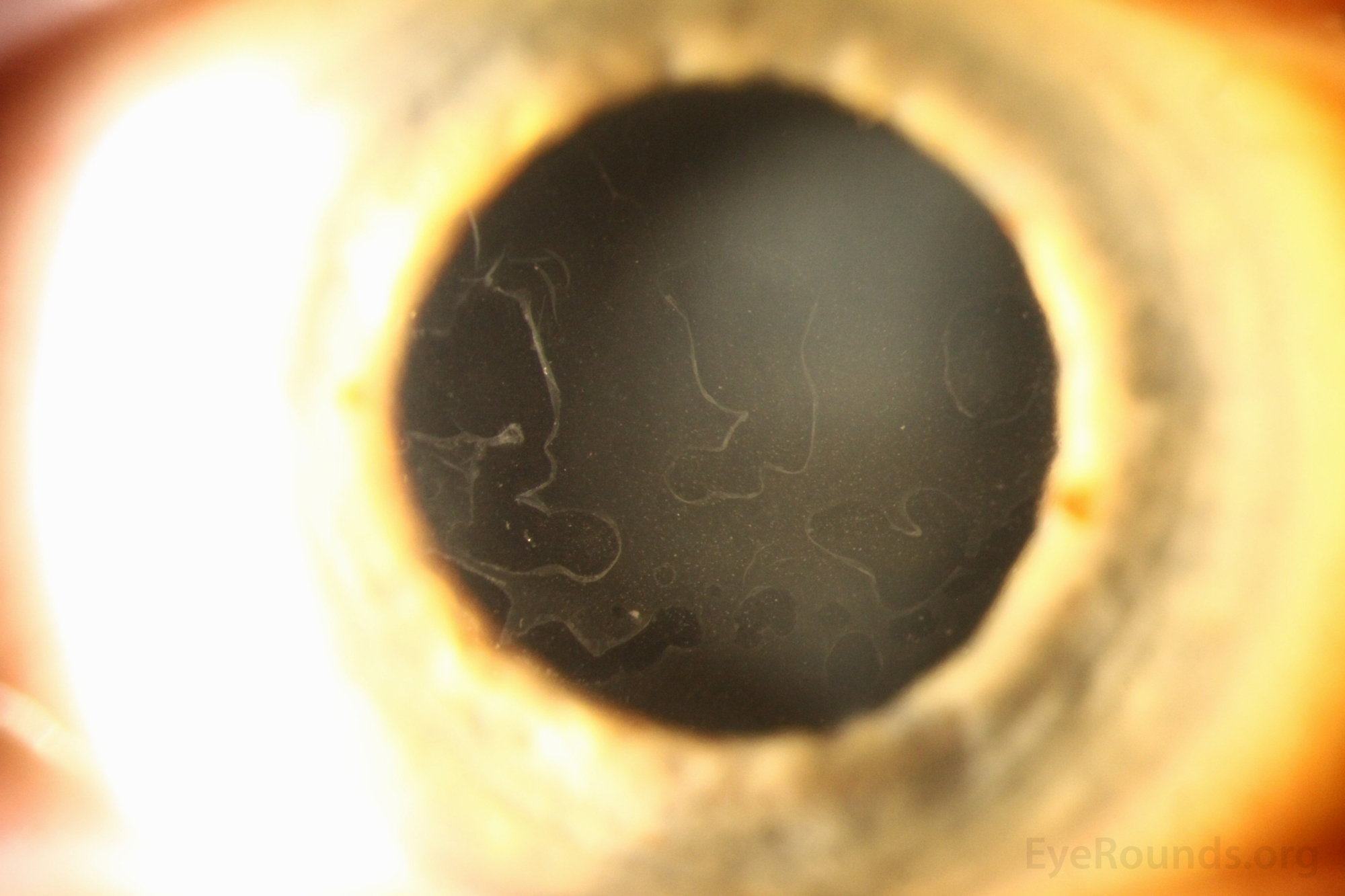
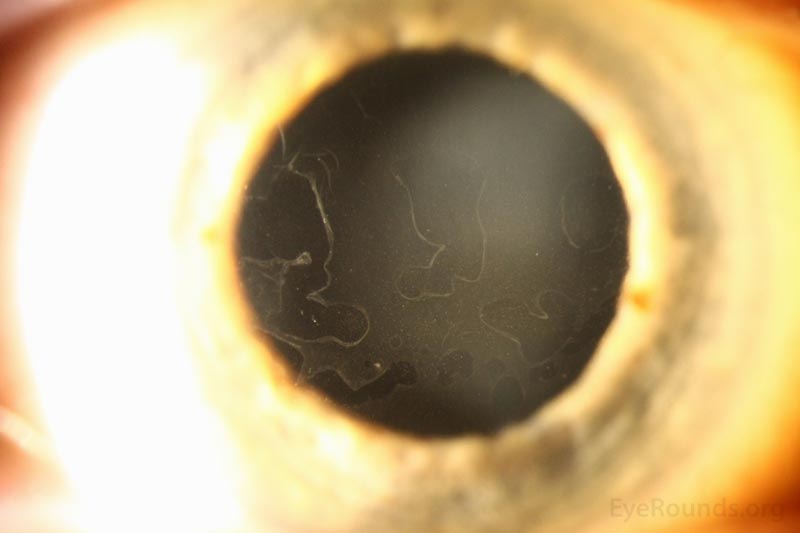
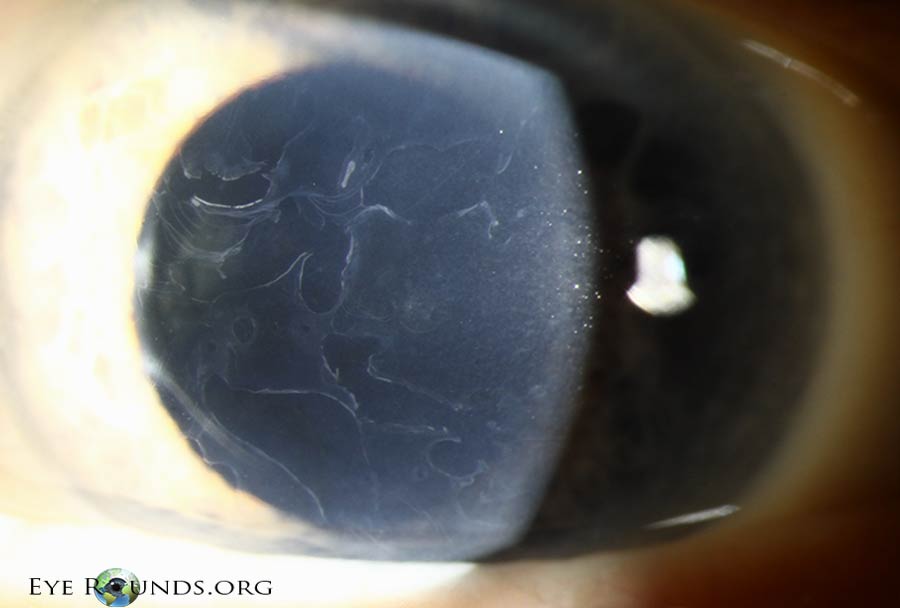
Map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy (MDFD) is a uncommon, inherited corneal dystrophy characterised by its distinctive medical look. The title itself hints on the distinctive sample of opacities that develop on the cornea, resembling a geographical map, scattered dots, and fingerprint-like whorls. Whereas seemingly a purely beauty concern, MDFD can considerably affect imaginative and prescient, resulting in lowered visible acuity, photophobia (gentle sensitivity), and even corneal blindness in extreme circumstances. This text offers a complete overview of MDFD, protecting its etiology, medical presentation, analysis, administration, and ongoing analysis.
Etiology and Genetics:
MDFD is primarily an autosomal dominant inherited dysfunction, which means a single copy of the mutated gene from both mum or dad is ample to trigger the situation. Nearly all of circumstances are related to mutations within the TGFBI gene (remodeling progress issue beta-induced gene), particularly inside exon 4. This gene codes for a protein known as βig-h3, a element of the corneal stroma, the cornea’s center layer accountable for its transparency and structural integrity. Mutations in TGFBI result in the irregular deposition of βig-h3, ensuing within the attribute opacities seen in MDFD.
Totally different mutations inside TGFBI can result in variations within the severity and development of MDFD. Some mutations trigger a milder type of the illness, whereas others may end up in extra extreme visible impairment. The age of onset and fee of illness development additionally fluctuate relying on the precise mutation. This genetic heterogeneity contributes to the medical variability noticed amongst people with MDFD. Curiously, some households exhibit a extra extreme phenotype, usually termed lattice corneal dystrophy kind I (LCD1), which shares vital overlap with MDFD however sometimes presents with extra in depth lattice-like opacities. The excellence between LCD1 and MDFD can generally be blurry, making correct genetic testing essential for exact analysis.
Scientific Presentation:
MDFD sometimes manifests within the first to 3rd many years of life, though the age of onset can fluctuate significantly. The preliminary presentation usually entails refined, asymptomatic opacities within the central or peripheral cornea. These opacities step by step enhance in dimension and density over time, evolving into the attribute map-like, dot-like, and fingerprint-like patterns that outline the situation.
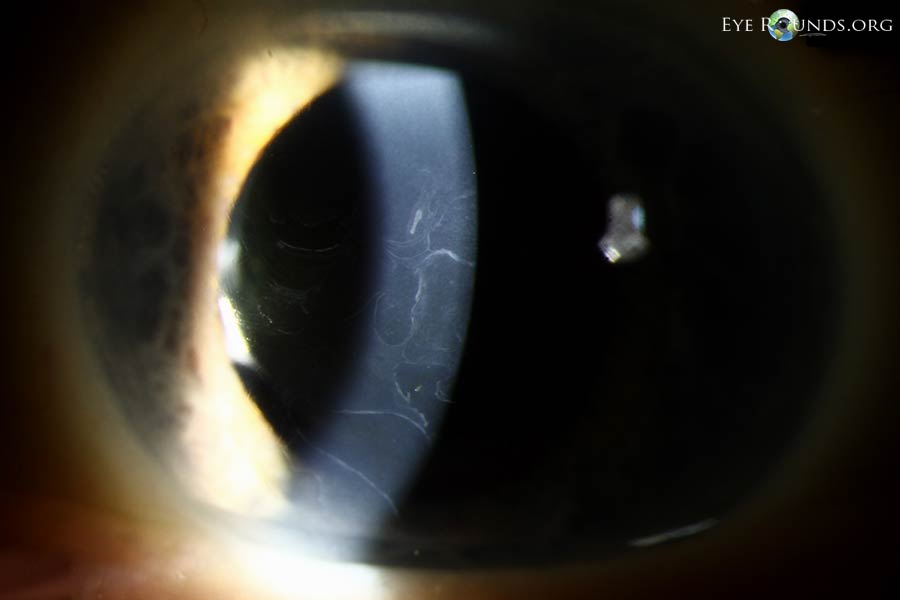
The "map" refers back to the geographical distribution of opacities, usually involving branching and interconnected traces resembling a topographical map. The "dots" are small, discrete opacities scattered all through the cornea. The "fingerprint" sample consists of whorled or concentric traces, paying homage to fingerprints. These patterns will not be at all times current in each particular person, and their prominence can fluctuate.
Because the illness progresses, the corneal opacities can change into extra dense and in depth, resulting in vital visible impairment. Sufferers might expertise lowered visible acuity, glare, and photophobia. Corneal haze and scarring may develop, additional compromising imaginative and prescient. In extreme circumstances, the opacities can cowl a good portion of the cornea, leading to appreciable visible loss and probably resulting in corneal blindness. Nonetheless, it is necessary to notice that the development of MDFD varies tremendously between people, and a few might expertise comparatively delicate signs all through their lives.
Analysis:
The analysis of MDFD is based totally on medical examination. A complete ophthalmologic analysis, together with an in depth historical past, visible acuity evaluation, slit-lamp biomicroscopy (a specialised microscope used to look at the attention), and corneal topography (mapping the corneal floor), is important. Slit-lamp biomicroscopy permits for visualization of the attribute corneal opacities, confirming the medical analysis of MDFD. Corneal topography may help assess the extent and severity of corneal involvement.
Genetic testing can affirm the analysis and determine the precise TGFBI mutation accountable for the situation. That is notably helpful in households with a historical past of MDFD, enabling predictive testing for at-risk people. Genetic testing additionally helps differentiate MDFD from different corneal dystrophies with related medical displays, corresponding to lattice corneal dystrophy, granular corneal dystrophy, and Avellino dystrophy. These situations share overlapping medical options, making genetic evaluation essential for exact analysis and administration.
Administration and Remedy:
Presently, there isn’t a treatment for MDFD. Administration focuses on assuaging signs and preserving visible operate. Remedy choices fluctuate relying on the severity of the illness and the person’s wants.
For delicate circumstances with minimal visible impairment, common ophthalmologic monitoring is normally ample. Sufferers ought to be suggested to guard their eyes from ultraviolet (UV) radiation and put on sun shades to attenuate photophobia. Synthetic tears or lubricating eye drops may help alleviate dryness and discomfort.
In average to extreme circumstances with vital visible impairment, numerous therapeutic interventions could also be thought of. Penetrating keratoplasty (PKP), a surgical process involving the alternative of the diseased cornea with a wholesome donor cornea, is a possible choice for sufferers with vital visible impairment resulting from central corneal opacification. Nonetheless, PKP carries inherent dangers and isn’t at all times profitable. Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK) is a much less invasive surgical different that replaces solely the affected layers of the cornea, lowering the dangers related to PKP. Each PKP and DALK are main surgical interventions and ought to be rigorously thought of primarily based on particular person circumstances.
Phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) is a much less invasive process that makes use of an excimer laser to take away the superficial corneal opacities. Whereas PTK can enhance visible acuity in some circumstances, it’s not a everlasting resolution and will must be repeated. Corneal collagen cross-linking (CXL) is a comparatively new therapy that strengthens the cornea, probably slowing the development of the illness. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of CXL in MDFD remains to be beneath investigation.
Ongoing Analysis and Future Instructions:
Analysis into MDFD is ongoing, specializing in a number of key areas. Scientists are actively investigating the exact mechanisms by which TGFBI mutations result in the irregular deposition of βig-h3 and the event of corneal opacities. This understanding is essential for creating novel therapeutic methods. Gene remedy holds appreciable promise as a possible treatment for MDFD. Gene remedy goals to appropriate the underlying genetic defect by introducing a purposeful copy of the TGFBI gene into the corneal cells. A number of preclinical research have proven promising outcomes, however additional analysis is required to translate these findings into protected and efficient medical remedies.
The event of latest surgical methods and improved therapeutic brokers can be a spotlight of ongoing analysis. Researchers are exploring much less invasive surgical procedures that reduce dangers and issues. The event of novel pharmacological brokers that focus on the underlying molecular mechanisms of MDFD might supply new therapeutic choices.
Conclusion:
Map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy is a uncommon however vital corneal dysfunction that may trigger appreciable visible impairment. Whereas there may be at present no treatment, advances in genetic testing, surgical methods, and ongoing analysis supply hope for improved administration and potential future therapies. Early analysis and common ophthalmologic monitoring are essential for managing the illness and preserving visible operate. Sufferers with MDFD ought to work carefully with their ophthalmologist to develop a personalised administration plan that addresses their particular person wants and targets. Additional analysis is important to totally perceive the pathophysiology of MDFD and develop efficient remedies that may forestall visible loss and enhance the standard of life for people affected by this situation.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Map Dot Dystrophy: A Complete Overview of this Uncommon Ocular Dysfunction. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!